
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, where efficiency and accuracy are paramount, understanding and implementing standardized business practices is key. One such standard that plays a crucial role in the retail industry is GS1, or Global Standards 1. In this article, we’ll delve into the significance of GS1, its impact on the retail landscape, and how it facilitates seamless business operations.
The Origins of GS1
GS1 is a global, non-profit organization that develops and maintains standards for business communication. These standards are designed to improve the efficiency, safety, and visibility of supply chains across various industries, with a particular focus on retail.
 GS1 has its origins in the development of the Universal Product Code (UPC), which was created in the early 1970s to address the challenges of inventory management and checkout processes in the retail industry. The idea for a standardized barcode system originated from a collaboration between Bernard Silver, a graduate student at Drexel Institute of Technology, and Norman Joseph Woodland, his mentor.
GS1 has its origins in the development of the Universal Product Code (UPC), which was created in the early 1970s to address the challenges of inventory management and checkout processes in the retail industry. The idea for a standardized barcode system originated from a collaboration between Bernard Silver, a graduate student at Drexel Institute of Technology, and Norman Joseph Woodland, his mentor.
The two men developed a system that used a series of concentric circles to encode data, which was later adapted into the barcode system we are familiar with today. In 1974, the first item with a barcode, a pack of Wrigley’s chewing gum, was scanned at a supermarket in Troy, Ohio, marking the beginning of the UPC system’s implementation.
From there, industry leaders recognized the need for a global organization to oversee and standardize the use of barcodes. This led to the creation of the Uniform Code Council (UCC) in the United States. Over time, the organization expanded its scope internationally, and in 2005, it officially became GS1 to reflect its global reach.
At the heart of GS1’s significance is its ability to revolutionize the retail landscape. By providing a common language for business processes, GS1 facilitates seamless communication and collaboration across the supply chain. This standardized approach ensures that every player in the retail ecosystem, from manufacturers to retailers and logistics providers, can operate on a unified platform.
Impact on Business Operations
GS1’s influence in the retail sector is profound. By providing a standardized language for business communication, GS1 facilitates accurate and timely information exchange between trading partners. This, in turn, streamlines processes like inventory management, order fulfillment, and logistics, fostering a more transparent and efficient supply chain. The following section delineates these key contributions.
Precision in Product Identification: Integral to GS1 is the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN), a unique identifier assigned to products and services. This alphanumeric code, along with other GS1 identification keys, such as the Global Location Number (GLN) and Serial Shipping Container Code (SSCC), ensures that each item is unmistakably distinguished. This not only simplifies inventory management but also reduces the risk of errors in product tracking and traceability.
Efficient Supply Chain Management: In the dynamic world of retail, where the speed of operations is a competitive advantage, GS1 standards streamline supply chain management. The adoption of standardized barcodes not only facilitates real-time inventory tracking but also significantly expedites the crucial process of picking and packing orders, driving operational and organizational efficiencies.
Enhanced Customer Experience: The seamless operations facilitated by GS1 directly contribute to an enhanced customer experience. From accurate inventory levels to efficient and accurate order fulfillment, customers benefit from the reliability and transparency that GS1 brings to the retail process. This, in turn, builds trust and loyalty among consumers.
Global Connectivity: In an era where businesses operate on a global scale, GS1’s role in providing global interoperability is paramount. With over 2 million member companies spanning 150 countries, the standards set by GS1 ensure that products can be easily identified and tracked across borders, fostering a cohesive and efficient global supply chain.
The Crucial Role of Barcoding in eCommerce Fulfillment

Utilizing the standards set forth by GS1, barcoding serves as a vital conduit, streamlining fulfillment operations and connecting various facets of the supply chain. From the moment products are received during inbound logistics, to the meticulous scanning of each item during outbound fulfillment, uniform barcodes enable eCommerce businesses to navigate the complexities of inventory management and order processing with unparalleled accuracy. This data-driven approach empowers businesses to make informed decisions, adapt to customer preferences, and optimize their supply chain strategies. Particularly in the context of third-party fulfillment, where entities may not own the products they handle, the unifying language of barcoding ensures that inventory is managed efficiently, product movements are meticulously tracked, and orders are fulfilled with the speed and precision required to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced eCommerce landscape. This symbiotic relationship between GS1 standards and barcoding not only streamlines operations, but also stands as a testament to the indispensable role they play in advancing the efficiency and collaboration essential for success in modern eCommerce.
GS1’s Future Outlook
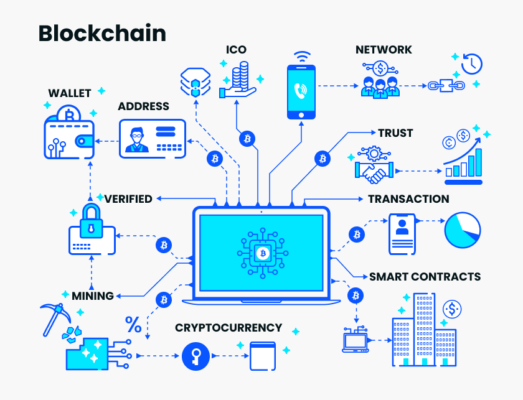
Looking forward, the retail sector’s future with GS1 holds promising prospects. Dynamic technologies like blockchain are positioned to advance the standardization and security of business communication, presenting the potential for a significant transformation. This advancement opens new avenues for bolstering data security and fostering advanced analytics within the retail landscape.
In conclusion, GS1’s journey from the development of the UPC system to its current status as a global standard for business communication reflects its profound impact on the retail landscape. By embracing GS1 standards, businesses can not only streamline their operations but also contribute to a more transparent and efficient global supply chain.
 5 Logistics
5 Logistics